Asynchronous Programming in .NET - The quick and easy way
When working on a program that has a GUI, it’s very important to make sure that the UI is fast and responsive. If your program is performing a lot of long-running actions (writing to a database, making network calls etc.) you should always make sure that the code that is performing those actions is not being executed by the same thread that the GUI is on.
The answer is of course asynchronous programming. Asynchronous code is executed on a different thread than your main one so that your main thread is free to do other things like draw pretty buttons and whatnot.
.NET makes it super easy to run code on a different thread - especially if you don’t care about the result. The function below just blocks whatever thread it’s on for a specified number of milliseconds.
Private Sub DoSomething(ByVal LengthInMilliseconds As Integer)
Thread.Sleep(LengthInMilliseconds)
Console.WriteLine("***** Work Complete *****")
End Sub
Now if you call this function on your main (UI) thread in a button click handler or something, the thread will block until the operation is complete. You need to call it on a different thread. Let’s create a new version of this function that will be asynchronous:
Private Sub DoSomethingAsync(ByVal LengthInMilliseconds As Integer)
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(AddressOf DoSomething, LengthInMilliseconds)
End Sub
Now you can call DoSomethingAsync from your main thread and it will be delegated out to a worker thread by the ThreadPool class. The ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem call is an extremely useful one-liner for asynchronous operations when you don’t care about the result.
I created a really simple Windows Forms project to demonstrate the code you see here.
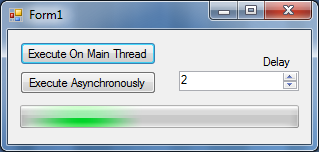
You can download this project (for VS2010) here.
To learn more, check out the resources on MSDN here: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.threading.threadpool.aspx